Nginx
Using Nginx as a reverse proxy and load balancer for Websocket traffic

This page needs to be improved/might be out of date! Raise a PR if you feel like adding a few details or totally revamping it.
What is nginx?
Nginx (pronounced engine-x) is a multi purpose webserver. It’s one of the most widely used HTTP servers and powers sites such as GitHub or reddit. Aside from serving static files via HTTP, it can be used as a reverse proxy, multi protocol load balancer or container for fast CGI scripts
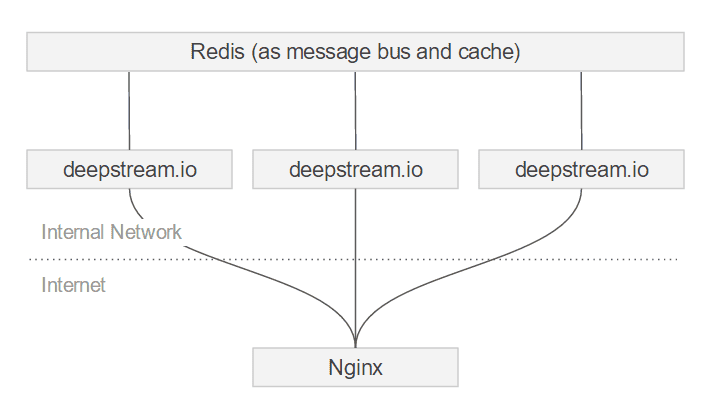
Using nginx and deepstream
Nginx can be used as a web-facing reverse proxy and load balancer in front of deepstream servers.
Reverse Proxy
For HTTP deployments it is common practice to not directly expose the webserver to the internet, but instead place a different server in front of it. For deepstream.io production deployments we highly recommend doing the same. This “reverse proxy” handles tasks like SSL termination (decrypting incoming messages via WSS ) and high availability / error reporting (e.g. replying to requests with a 500 status if the underlying server is unavailable).
Load Balancer
deepstream can scale horizontally via clustering. If you want to provide a single URL for clients to connect to your cluster, you need to place something in front that distributes incoming connections between the available servers: a load balancer. Load balancing persistent connections can be a bit tricky sometimes. deepstream supports connections made via WebSockets.
Alternatives to nginx
Instead of nginx you could also use e.g. HA Proxy or Apache
What about AWS Elastic Load Balancer?
If you’re deploying deepstream on AWS, you’d probably want to use Amazon’s well integrated load balancing service ALB. It allows you to combine ssl termination, load balancing and health-checks for easy deployment.
Installing nginx for use with deepstream
By default, Nginx comes with everything you need to use it as an HTTP server. To use it as a stream server though, you need to build it with its stream module enabled (--with-stream). On CentOS/AWS Linux this works as follows, for other Linux distributions, have a look here.
# install gcc (needed to compile nginx)
yum update
yum install -y aws-cli openssl-devel
# download and unzip nginx stable version (check for latest version number before using)
wget http://nginx.org/download/nginx-1.11.5.tar.gz
tar zxf nginx-1.11.5.tar.gz
mv nginx-1.11.5 nginx
cd nginx
# enable stream, disable unneeded http modules that require additional dependencies
./configure --with-stream --with-stream_ssl_module --without-http_rewrite_module --without-http_gzip_module
# build and install
make installConfiguring nginx as a stream proxy / load balancer
In V5 you can see the recommended configuration file by running:
deepstream nginx
Usage: deepstream nginx [options]
Generate an nginx config file for deepstream
Options:
-c, --config [file] The deepstream config file
-p, --port The nginx port, defaults to 8080
-h, --host The nginx host, defaults to localhost
--ssl If ssl encryption should be added
--ssl-cert The SSL Certificate Path
--ssl-key The SSL Key Path
-o, --output [file] The file to save the configuration to
-h, --help output usage informationThis will generate the desired output from your config file.
Manual configuration
The following configuration shows how to use nginx as a load balancer, SSL termination point and reverse proxy for HTTP, WS and TCP connections. If you only want to use parts of this functionality, remove the unneeded bits.
worker_processes 1;
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
http {
map $http_upgrade $connection_upgrade {
default upgrade;
'' close;
}
upstream deepstream {
server localhost:6020;
}
server {
listen 9090 ssl;
server_name localhost;
ssl_protocols TLSv1 TLSv1.1 TLSv1.2;
ssl_ciphers HIGH:!aNULL:!MD5;
ssl_certificate /etc/ssl/certs/cert.crt;
ssl_certificate_key /etc/ssl/certs/key.key;
# Deepstream websocket redirect
location /deepstream {
proxy_pass http://deepstream;
proxy_http_version 1.1;
proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade;
proxy_set_header Connection "Upgrade";
}
# Deepstream http endpoint
location /api {
proxy_pass http://deepstream;
proxy_http_version 1.1;
}
}
}